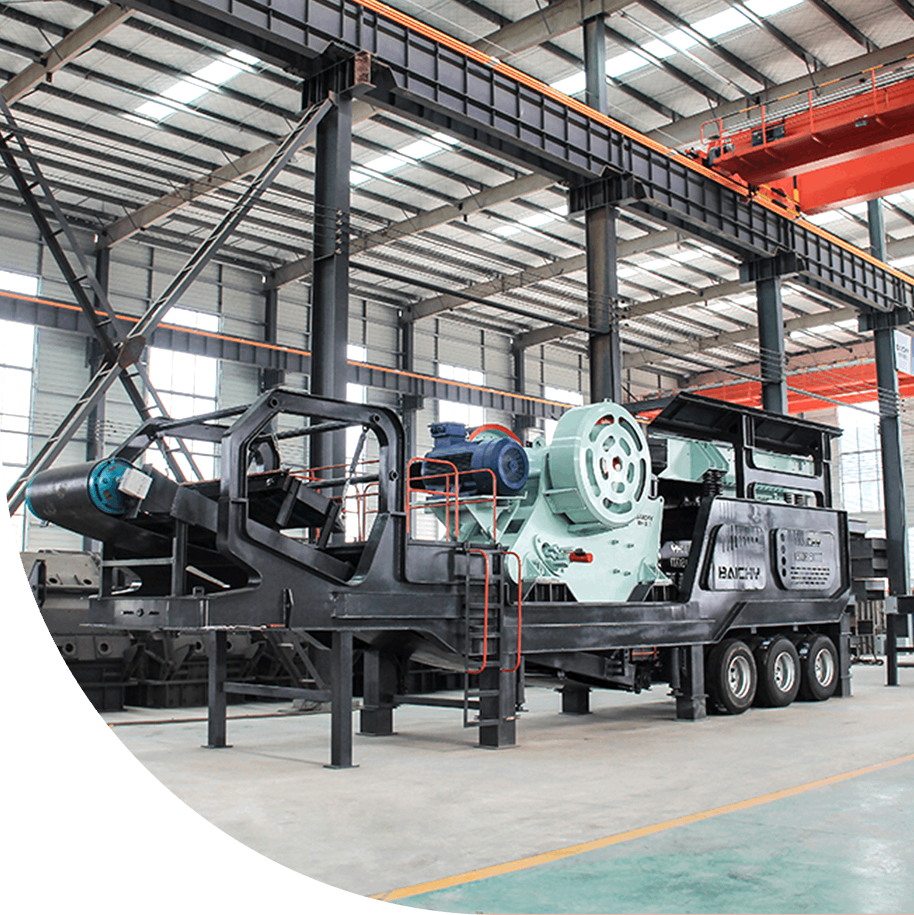
Energy Saving Ball mill
Energy saving ball mill is a crucial piece of equipment used in mineral processing operations to grind mined ore into fine particles. These rotating cylindrical machines use steel balls as grinding media to break down ore materials, facilitating the extraction of valuable minerals. It operates on the principle of reducing particle size through the impact and attrition of grinding media within a rotating cylinder. This versatile machine plays a crucial role in processes ranging from mineral processing to pharmaceutical production.
-
0-25 mm
Feed Size
-
0.65-800 KW
Motor Power
-
0.5-90 t/h
Processing Capacity