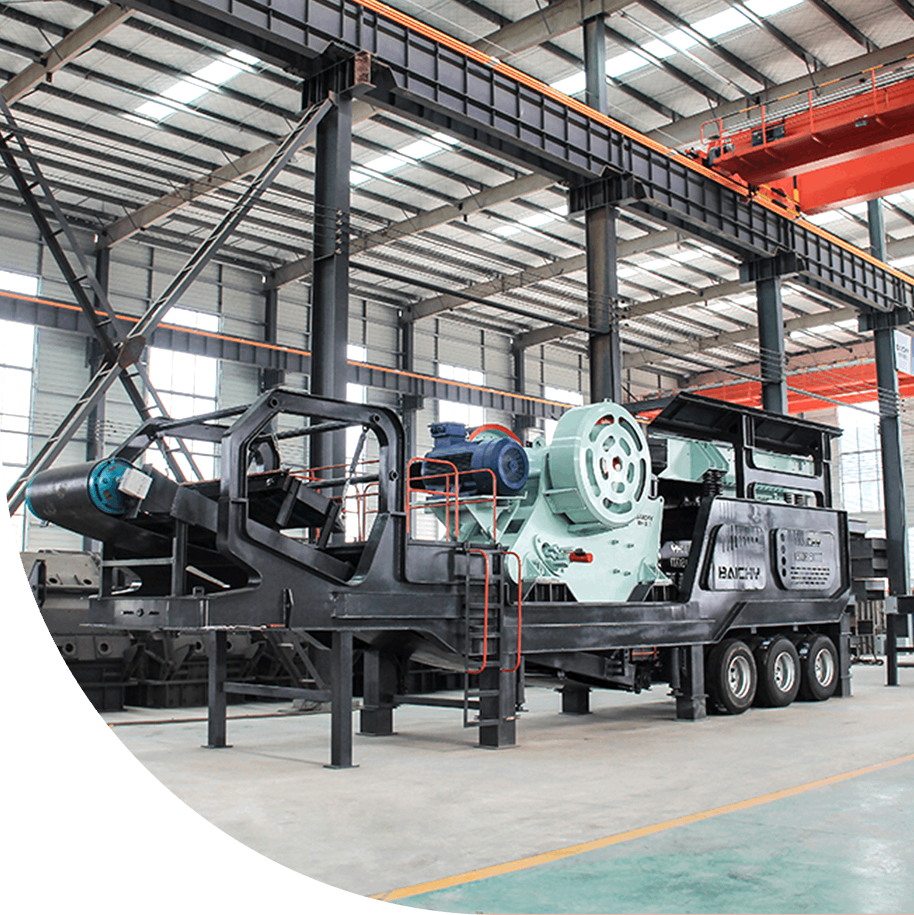
Shaking Table
A shaking table, also known as a gravity shaking table or mineral separation table, is a gravity-based separation device used to separate fine minerals based on differences in density, particle size, and shape. It operates by stratifying mineral particles on a sloped, oscillating deck, allowing heavier minerals (e.g., gold, tin, tungsten) to settle and move along the table while lighter gangue minerals are washed away.
-
0-2 mm
Feed Size
-
1.1 kw
Motor Power
-
10-60 tph
Processing Capacity